

Welcome to the world of modern techniques for requirements elicitation in product discovery! In this first part of our series, we explore the transformative shift in mindset and methodology that revolutionizes how product teams approach requirements gathering and innovation.
In product management, requirements elicitation has transformed simply gathering stakeholders' wishes into discovering innovative solutions to their problems. This shift in mindset has given rise to the adoption of modern techniques in product discovery. This blog delves into these techniques and their alignment with the three types of requirements: business, stakeholder, and solution.
Requirements play a crucial role in the success of any project or system development. To manage and prioritize these requirements effectively, the International Requirements Engineering Board (IREB) has classified them into business, user, and system requirements. Each category serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall understanding and implementation of the project.

Business requirements capture the overarching goals and objectives of an organization. They provide a project's context and strategic direction, guiding the decision-making process. Business requirements answer the fundamental questions of why a project is being undertaken and what the business aims to achieve. They outline the desired outcomes and benefits from a business perspective, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization's strategic goals.
User requirements focus on the needs and expectations of the stakeholders who will interact with the system. They represent the features, functions, and behaviors that the system should exhibit from the perspective of its users. User requirements serve as a bridge between the high-level business goals and the technical details of system design. By understanding and incorporating user requirements, organizations can ensure that the system meets the needs and preferences of its intended users, enhancing user satisfaction and usability.

System requirements specify the technical specifications and constraints the system must adhere to to meet the user and business requirements. These requirements cover various aspects, including software functionalities, hardware specifications, performance metrics, and other technical characteristics necessary for the successful implementation and operation of the system. System requirements ensure that the system is designed, developed, and deployed to align with the desired technical specifications and constraints, ensuring its reliability, scalability, and performance.
Traditionally, requirements gathering involved compiling a list of desired features and functionalities from stakeholders. However, this approach is being supplanted by a more collaborative and experimental mindset. Product teams now recognize the significance of uncovering stakeholders' underlying problems and needs.
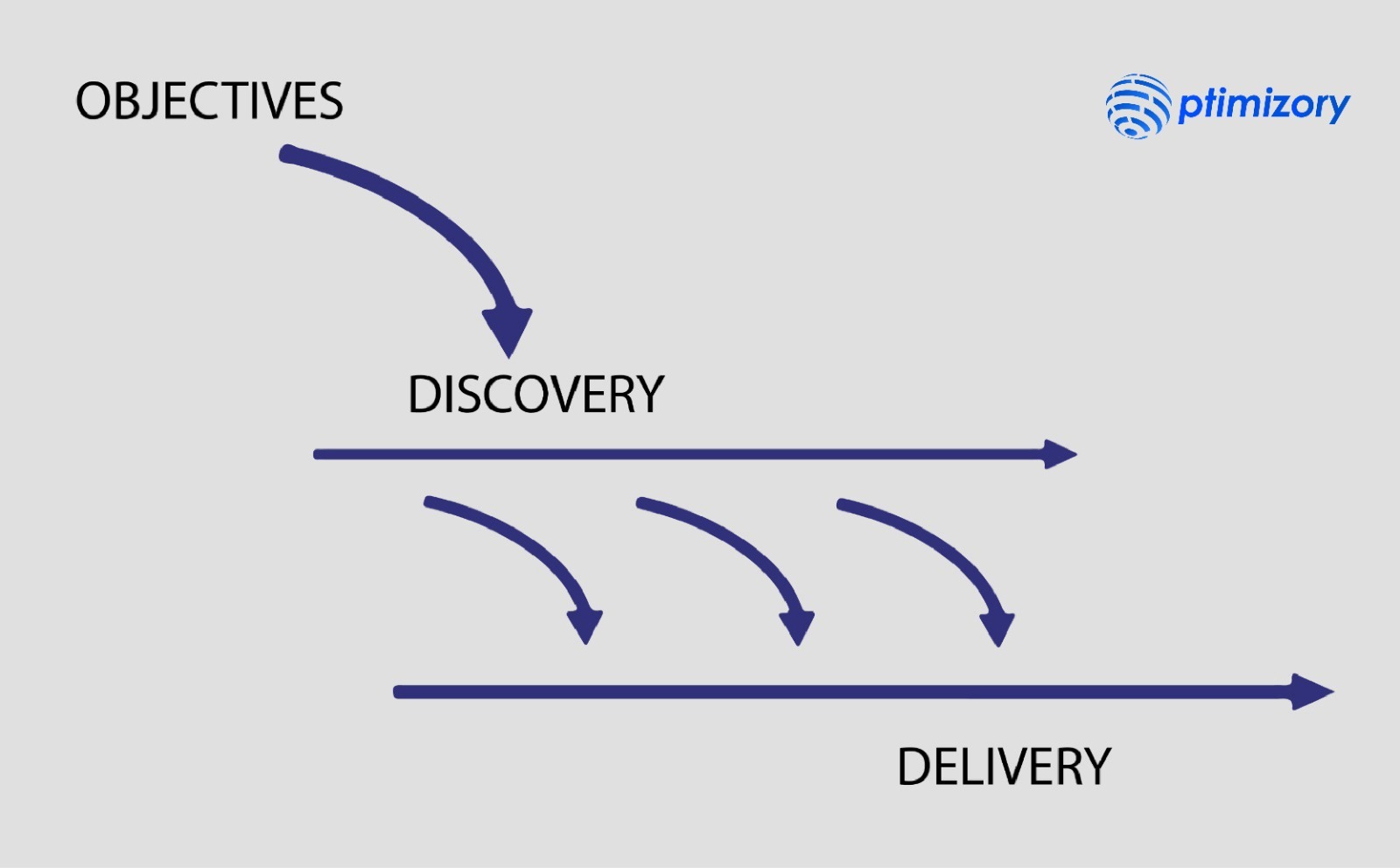
Frameworks like Dual Track Agile have emerged to underscore the importance of both product discovery and delivery. This approach divides efforts into two tracks: one focused on discovering the optimal solution and the other on effectively delivering the solution.
Eliciting business requirements is the process of gathering and understanding a business or organization's needs, goals, and objectives. It involves identifying and documenting the specific features, functionalities, and constraints a product or service should have to meet the business's objectives.
The techniques for eliciting business requirements are designed to facilitate effective communication and collaboration between stakeholders and the product team. These techniques help uncover and clarify the business's needs, ensuring that the resulting product or service aligns with the organization's goals. Some standard techniques for eliciting business requirements include:
The "How Might We" technique is a valuable tool in the design thinking process for framing problem statements and generating creative solutions. It is commonly used in design sprints, which are collaborative and time-constrained processes to solve complex problems and develop innovative solutions. This technique, popularized by design firm IDEO, is widely employed in design workshops, brainstorming sessions, and innovation processes.
The "How Might We" technique transforms challenges or problem areas into open-ended questions that stimulate brainstorming and encourage creativity. This technique prompts teams to think beyond constraints and explore a wide range of potential solutions. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how the technique works:
By utilizing the "How Might We" technique, teams can foster a creative and collaborative environment that encourages innovative thinking. It helps reframe challenges as opportunities for exploration and generates many potential solutions.
JTBD is a framework that aids in comprehending why customers "hire" a particular product or service. It centers on defining desired outcomes and understanding the circumstances and emotional dimensions surrounding product usage. Product teams can align their solutions more effectively with customer needs by identifying various customer jobs and their corresponding desired outcomes. A template from Jurgen Appelo to write the JTBD is shown in the figure below.

In conclusion, the evolution of requirements elicitation from a mere list of stakeholder wishes to a deep understanding of underlying problems has reshaped the landscape of product discovery.
By embracing modern techniques and frameworks, product teams can navigate the dynamic landscape of innovation, forge new pathways to success, and deliver value that transcends expectations. In the journey from requirements elicitation to product discovery, the quest for understanding and innovation continues to fuel the engine of progress, propelling organizations toward greater achievement and impact.
Stay tuned for the second part of our series, where we delve into techniques for eliciting user requirements and explore innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and solving complex problems.